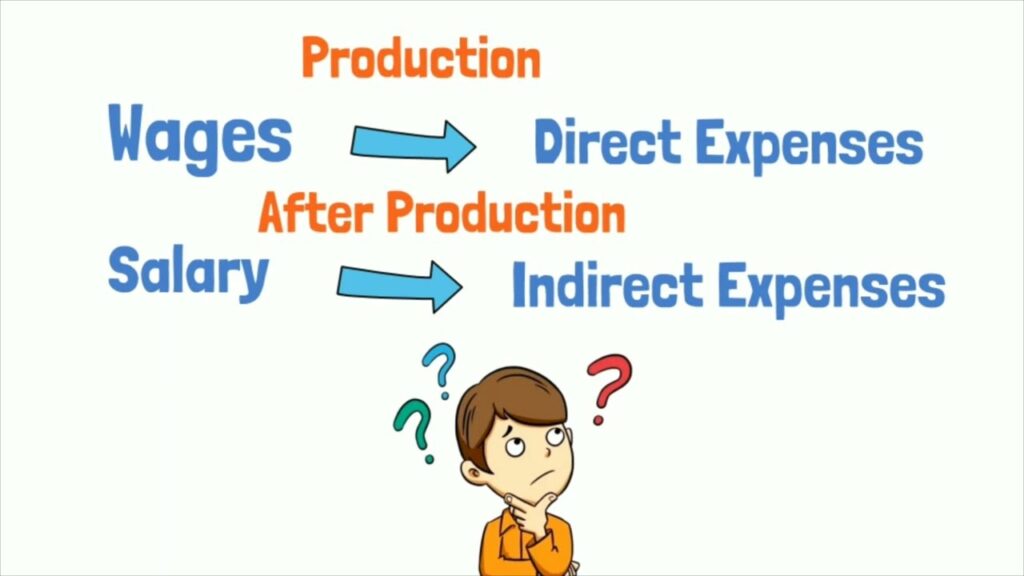
Direct and Indirect Expenses
Before diving into the specifics of salaries and wages, it’s essential to understand the basic definitions of direct and indirect expenses:
Direct Expenses:
These are expenses that can be specifically linked to the creation of goods or the provision of services. They vary depending on the level of production. In other words, if production increases, direct expenses will likely increase as well.
Indirect Expenses:
These are costs that cannot be directly linked to the production of a specific product or service. These expenses generally stay the same, irrespective of changes in production or sales levels.
Now, let’s examine where salaries and wages fit into these categories.
Wages as Direct Expenses
Wages are typically classified as direct expenses for several reasons:
Directly Tied to Production:
Wages are paid to employees who are involved directly in the production process. This could be factory workers, machine operators, or assembly line workers. Their work directly impacts the quantity of goods or services produced. Therefore, the cost of paying these employees can be directly traced to the product.
Variable Costs:
The cost of wages can fluctuate depending on the level of production. For instance, if a company needs to produce more units, it may require more labor hours, and thus, the wages paid out will increase accordingly.
Easily Traceable to Output:
Since wages are paid based on the hours worked or tasks completed, they can be easily traced to the output. If a company manufactures 100 units of a product, the wages paid for labor directly involved in the production of those units can be attributed as a direct cost.
Salaries as Indirect Expenses
Salaries, on the other hand, are generally categorized as indirect expenses because:
Not Directly Linked to Production:
Salaries are paid to employees who are not directly involved in the production process. These employees might include managers, administrative staff, HR personnel, and office workers. While they play a crucial role in running the business, their work is not tied to the actual creation of products or services.
Fixed Costs:
Unlike wages, salaries tend to be fixed costs. Whether a company produces 100 units or 1,000 units, the salaries of its office and management staff remain the same. Therefore, these costs are not directly linked to the level of production.
Supporting Role:
Employees who receive salaries generally provide support to the production process rather than contributing directly. For instance, a company’s marketing team, while important, doesn’t directly affect how many units are produced but helps promote the product. Thus, their salaries are classified as indirect expenses.
Why the Classification Matters
Understanding the difference between direct and indirect expenses, and how salaries and wages fit into these categories, is important for several reasons:
Cost Allocation:
In cost accounting, businesses allocate expenses to different products or departments to determine profitability. Since wages are directly tied to production, they can be allocated to specific products or services. Salaries, on the other hand, are allocated as overhead or indirect costs.
Pricing and Profitability:
Direct expenses like wages impact the cost of producing goods and can therefore influence the pricing of products. Indirect expenses, such as salaries, need to be factored into the overall business overhead and are usually spread across all products or services.
Financial Reporting:
Companies need to differentiate between direct and indirect expenses when preparing financial statements. This distinction helps in understanding how much it costs to produce goods and services and how much is spent on operating the business as a whole.
Real-World Example
Consider a company that manufactures smartphones:
The wages paid to the factory workers assembling the phones would be classified as direct expenses. These costs increase with the number of phones produced.
The salaries paid to the marketing team or the HR department would be considered indirect expenses. These costs remain relatively constant, regardless of how many phones the factory produces.
Conclusion
The distinction between salaries and wages as indirect and direct expenses, respectively, lies in their relationship to production. Wages are tied directly to the creation of goods and services, making them a direct expense, while salaries support business operations in a broader sense, categorizing them as indirect expenses. Recognizing this difference is essential for accurate cost allocation, pricing, and financial management in any business.
FAQs
To visit: https://www.incometax.gov.in
For further details Visit: https://vibrantfinserv.com/service-detail-25.php
Contact: 8130555124, 8130045124
Whatsapp: https://wa.me/918130555124
Mail ID: operations@vibrantfinserv.com
Web Link: https://vibrantfinserv.com
FB Link: https://fb.me/vibrantfinserv
Insta Link: https://www.instagram.com/vibrantfinserv2/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/VibrantFinserv
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vibrant-finserv-62566a259/