![]()
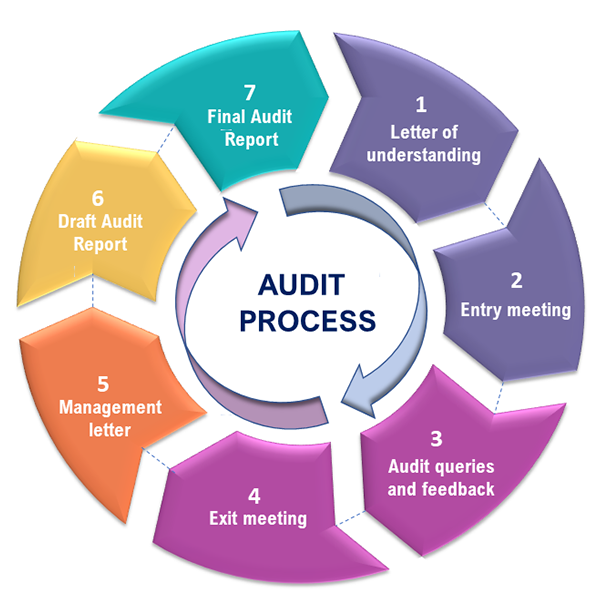
The process of auditing
Auditing is a process of examining the financial records, operations, and activities of an organization to provide an independent opinion on whether the financial statements provide a true and fair view of the organization’s financial position and performance.
The following are the general steps involved in the auditing process:
1.Planning: The auditor plans the audit, which includes understanding the business, assessing the risks, and determining the audit scope and objectives.
To visit- https://www.mca.gov.in/
2.Risk assessment: The auditor assesses the risks associated with the organization’s financial statements, including the risk of fraud, error, and misstatement.
3.Evidence collection: The auditor collects sufficient and appropriate evidence to support the audit opinion. This may involve examining financial records, interviewing staff, observing operations, and testing controls and procedures.
4.Analysis and evaluation: The auditor analyzes and evaluates the evidence collected, comparing it against the audit objectives and relevant accounting standards.
5.Reporting: The auditor prepares an audit report, which includes the audit opinion on whether the financial statements provide a true and fair view of the organization’s financial position and performance, and any significant findings or issues identified during the audit.
6.Follow-up: The auditor may also provide recommendations for improvements to the organization’s financial reporting and control systems and follow up on the implementation of these recommendations in subsequent audits.
The specific steps involved in the auditing process may vary depending on the nature of the organization, the size of the audit, and the applicable audit standards and regulations.
FAQs:
What is the auditing process?
The auditing process involves a series of steps to systematically examine and evaluate financial records and operations for accuracy and compliance.
What are the initial steps in an audit?
The initial steps include planning the audit, understanding the client’s business, and assessing risk factors.
What does the planning phase involve?
The planning phase involves setting objectives, determining the scope of the audit, and developing an audit strategy.
How do auditors gather evidence?
Auditors gather evidence through various methods, including inspection, observation, inquiries, and analytical procedures.
What is the role of internal controls in the auditing process?
Internal controls are assessed to determine their effectiveness in preventing errors and fraud.
Influencing the auditor’s approach.
What happens during the fieldwork phase?
During fieldwork, auditors perform the actual examination of financial records, collect evidence, and conduct tests on transactions.
How is audit evidence evaluate?
Audit evidence is evaluated based on its relevance, reliability, and sufficiency to support the auditor’s findings and conclusions.
What is the reporting phase in auditing?
The reporting phase involves compiling the findings and issuing an audit report that communicates the auditor’s opinion on the financial statements.
What is include in an audit report?
An audit report typically includes the auditor’s opinion, a summary of audit findings, and any recommendations for improvements.
What is the follow-up process after an audit?
The follow-up process may involve reviewing management’s responses to the audit findings.
Monitoring the implementation of recommendations, and conducting subsequent audits as necessary.
For further details access our website https://vibrantfinserv.com/
