The meaning of Trademark and Copyright
What is a Trademark?
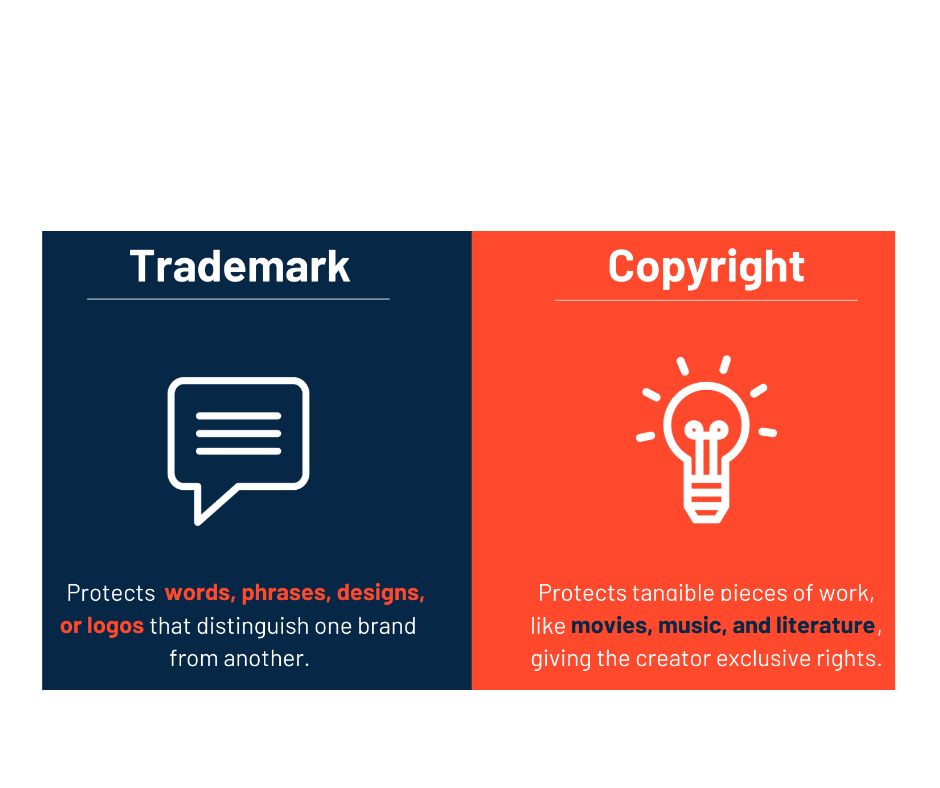
A trademark is a sign capable of distinguishing the goods or services of one enterprise from those of other enterprises. It can be a word, phrase, symbol, design, or a combination of these elements used to identify and protect brand names, logos, and slogans.
Key Aspects of Trademarks:
- Purpose: The primary purpose of a trademark is to help consumers identify and distinguish products or services from one another. It helps build brand recognition and loyalty.
- Types: Trademarks can be words (like “Apple”), logos (like the Nike swoosh), slogans (like “Just Do It”), or even sounds and colors in some cases.
- Registration: While common law rights to a trademark can be established through use, formal registration with a trademark office (such as the United States Patent and Trademark Office, or USPTO) provides additional legal protections and exclusive rights.
- Duration: Trademark rights can last indefinitely, as long as the trademark is in use and renewal fees are paid.
Example of a Trademark:
The “Coca-Cola” name and its distinctive script logo are trademarks. They distinguish Coca-Cola’s beverages from those of other manufacturers and signify the brand’s quality and reputation.
What is Copyright?
Copyright is a legal right that grants the creator of original works of authorship exclusive rights to their creation. This includes literary, musical, dramatic, and artistic works, among others. Copyright protects the expression of ideas, but not the ideas themselves.
Key Aspects of Copyright:
- Purpose: The primary purpose of copyright is to encourage the creation of art and culture by providing creators with the right to control the use and distribution of their works and to benefit financially from them.
- Types of Works: Copyright covers a wide range of works, including books, music, films, software, paintings, and architectural designs.
- Automatic Protection: Copyright protection is automatic upon the creation of the work and does not require registration, though registering can provide additional legal benefits.
- Duration: Copyright protection typically lasts for the life of the author plus 70 years. For works created for hire or corporate authorship, it generally lasts for 95 years from publication or 120 years from creation, whichever is shorter.
Example of Copyright:
An original novel written by an author is protected by copyright. The author has the exclusive right to reproduce, distribute, and adapt the work, and others must seek permission to use it.
Key Differences Between Trademark and Copyright
- Nature of Protection:
- Trademark: Protects brand identifiers like names, logos, and slogans used in commerce.
- Copyright: Protects original works of authorship and creative expressions.
- Purpose:
- Trademark: To prevent consumer confusion and protect brand identity.
- Copyright: To provide creators with exclusive rights to their creative works and encourage artistic and literary contributions.
- Scope:
- Trademark: Can be used for commercial purposes to differentiate products and services.
- Copyright: Covers the specific expression of ideas, not the underlying concepts.
- Registration:
- Trademark: Registration provides formal recognition and additional legal benefits.
- Copyright: Protection is automatic upon creation; registration is optional but advantageous.
- Duration:
- Trademark: Can last indefinitely with proper use and maintenance.
- Copyright: Has a set duration based on the creator’s life or publication date.
FAQs
1.What does a trademark protect?
Answer: A trademark protects brand names, logos, and symbols from being used without permission, ensuring consumers can identify the source of products or services.
2. What does copyright protect?
Answer: Copyright protects original works of authorship, such as literary, musical, and artistic works, preventing others from copying or using them without permission.
3. How long does trademark protection last?
Answer: Trademark protection can last indefinitely as long as it is actively used in commerce and renewal fees are paid.
4. How long does copyright protection last?
Answer: Copyright protection typically lasts for the life of the author plus 70 years, or for 95 years from publication or 120 years from creation for works created by corporations.
5. Can trademarks be register?
Answer: Yes, trademarks can be register with government authorities (e.g., the USPTO in the U.S.) to gain legal protection and exclusive rights.
6. Can copyright be register?
Answer: Yes, while copyright protection exists automatically upon creation, registering with a government authority (e.g., the U.S. Copyright Office) provides additional legal benefits and evidence of ownership.
7. Can a trademark be transfer or sold?
Answer: Yes, trademarks can be transferred or sold to other entities through a legal process.
8. Can copyright be transfer or sold?
Answer: Yes, copyright can be transfer or sold through licensing agreements or assignments, allowing others to use or control the copyrighted work.
For further details access our website: https://vibrantfinserv.com