Understanding tax planning is crucial for individuals and businesses to minimize tax liability legally and maximize financial efficiency. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of tax planning, covering its definition, applications, benefits, limitations, and comparisons.
Introduction
Taxes are an inevitable part of financial life, whether you’re an individual earning a salary or a business generating revenue. However, strategic tax planning can help you reduce your tax burden and increase savings. By understanding tax laws, exemptions, deductions, and benefits, you can create an efficient financial plan that aligns with your long-term goals. This guide will take you through the fundamental aspects of tax planning and how it can be applied effectively.
Definition
Tax planning is the process of analyzing an individual’s or business’s financial situation to legally minimize tax liability. It involves using available tax deductions, exemptions, and benefits in compliance with government regulations to optimize tax outcomes. It is a proactive approach to managing finances rather than reacting to tax obligations.
Application in Detail
Tax planning can be applied in various ways, depending on an individual’s or business’s financial situation. Types;
1. Short-term
- This involves taking actions towards the end of a financial year to reduce immediate tax liability.
- Example: Making last-minute investments in tax-saving instruments.
2. Long-term
- It includes financial strategies planned well in advance to ensure tax efficiency over an extended period.
- Example: Investing in retirement plans to get tax benefits over time.
3. Purposive
- This focuses on utilizing legal provisions to achieve financial goals while reducing tax liability.
- Example: Structuring salary components to maximize tax exemptions.
4. Permissive
- Using government-sanctioned benefits and deductions to optimize tax liability.
- Example: Claiming deductions under specific sections like 80C, 80D, etc.
Benefits in Detail
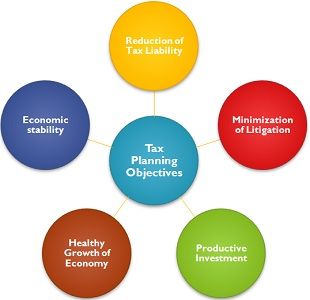
1. Reduced Tax Liability
Proper tax planning helps individuals and businesses legally lower their tax burden by utilizing deductions, exemptions, and rebates.
2. Increased Savings
By minimizing taxes, individuals can increase disposable income and businesses can reinvest the savings for growth.
3. Better Investment Planning
It encourages structured investments in instruments like mutual funds, insurance, and retirement plans that offer tax benefits.
4. Compliance with Tax Laws
Strategic tax planning ensures that individuals and businesses adhere to tax regulations, avoiding penalties and legal complications.
5. Financial Stability and Growth
For businesses, tax planning allows better resource allocation, leading to sustained financial growth and stability.
Limitations in Detail
1. Complexity in Implementation
- It requires extensive knowledge of tax laws and regulations, which can be challenging for a layperson.
2. Frequent Changes in Tax Laws
- Governments often update tax rules, making it necessary to stay informed and adjust tax strategies accordingly.
3. Risk of Non-Compliance
- Misinterpretation of tax laws may lead to unintentional tax evasion, resulting in penalties and legal issues.
4. Investment Restrictions
- Some tax-saving investments come with long lock-in periods, limiting liquidity and flexibility.
5. Professional Fees
- Hiring tax consultants or financial planners may involve additional costs that some individuals or small businesses may find burdensome.
For more information visit this site: https://www.incometax.gov.in
Comparative Table;
| Factor | Tax Planning | Tax Avoidance | Tax Evasion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legality | Legal | Legal (but unethical) | Illegal |
| Purpose | Reduce tax liability legally | Exploit loopholes | Evade taxes unlawfully |
| Consequences | Tax savings, compliance | Can lead to scrutiny | Penalties, fines, legal action |
| Example | Investing in tax-saving schemes | Using offshore accounts | Underreporting income |
Conclusion
It is a crucial aspect of financial management that helps individuals and businesses reduce tax burdens legally. By implementing the right tax strategies, one can optimize financial resources, ensure compliance with tax laws, and achieve long-term financial stability. However, it is important to stay informed about tax regulations and seek professional advice when necessary to avoid unintended legal consequences.
FAQs
1. What is the main objective of tax planning?
The main objective is to minimize tax liability while complying with tax laws and optimizing financial resources.
2. How does tax planning benefit businesses?
It helps businesses reduce expenses, reinvest savings, and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
3. Is tax planning legal?
Yes, tax planning is a legal practice as long as it follows government-approved tax-saving strategies.
4. Can tax planning help in retirement planning?
Yes, tax-saving investments like pension funds and retirement accounts can provide tax benefits while securing financial stability in the future.
For further details access our website: https://vibrantfinserv.com