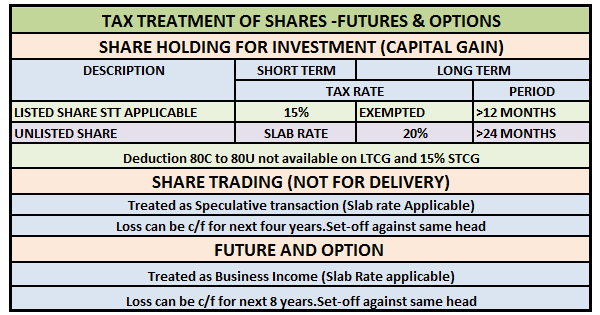
Introduction
Futures trading is an attractive option for investors looking to hedge risks or speculate on price movements. However, traders often overlook the tax implications associated with futures contracts, which can significantly impact profits and financial planning. Understanding these tax rules is essential for traders to maximize gains while ensuring compliance with tax laws.
Definition
Futures trading involves buying or selling contracts that obligate the trader to purchase or deliver an asset at a predetermined future date and price.Traders and investors widely use these contracts for commodities, stock indices, currencies, and other financial instruments.
Unlike stock trading, where tax implications are straightforward, futures trading has unique tax treatments, including special capital gains rates and tax-reporting methods.
User Intent
The primary goal of understanding the tax implications of futures trading is to ensure traders comply with tax laws while optimizing their financial strategies. Some common intents include:
- Learning about tax rates applicable to futures trading
- Understanding IRS tax rules for futures contracts
- Minimizing tax liabilities through strategic trading and tax planning
- Knowing reporting requirements to avoid penalties
Benefits of Understanding Tax Implications in Futures Trading
- Lower Tax Rates: Futures contracts often qualify for favorable tax treatment under IRS Section 1256, with 60% long-term and 40% short-term capital gains taxation.
- Tax Deferral Opportunities: Unlike stocks, where tax liabilities arise upon selling shares, futures contracts provide flexibility in taxation based on open positions and settlement.
- Loss Deduction: Traders can use capital losses from futures trading to offset gains, reducing overall tax burdens.
- Avoiding IRS Penalties: Proper understanding and reporting of futures trading taxes prevent costly penalties or audits.
Usage and Application
Futures trading taxation applies to various investor profiles, from retail traders to institutional investors. The IRS classifies futures contracts as Section 1256 Contracts, meaning they receive preferential tax treatment. Here’s how this classification applies:
- Tax Rate Benefits: The IRS taxes Section 1256 Contracts at a blended rate—60% as long-term capital gains (15%) and 40% as short-term capital gains (ordinary income tax rate), regardless of the holding period.
- The Mark-to-Market (MTM) rule: requires marking all open futures positions to market at the end of the tax year, realizing gains and losses even if the contract remains open.
- Carrying Over Losses: Losses from futures contracts can be carried forward to offset future profits, providing tax efficiency.
Limitations and Challenges
While tax benefits exist, there are limitations and challenges associated with futures trading taxation:
- Complex Tax Reporting: Traders must report gains and losses on IRS Form 6781, which can be complex for those unfamiliar with tax regulations.
- Unfavorable Tax Treatment for Non-Section 1256 Contracts: Not all derivatives enjoy the 60/40 tax benefit; some may be taxed as ordinary income.
- Wash Sale Rules: Unlike stocks, futures trading is largely exempt from wash sale rules, but certain IRS interpretations may apply in specific cases.
- International Tax Implications: For traders outside the U.S., tax rules may vary, requiring specialized tax planning.
- State Tax Considerations: Some states may have additional tax implications beyond federal requirements.
Cooperative Table: Tax Treatment Overview
| Aspect | Futures Trading (Section 1256) | Stock Trading (Capital Gains) |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Rate | 60% long-term, 40% short-term | Short-term: ordinary rate; Long-term: 15-20% |
| Reporting Form | IRS Form 6781 | IRS Schedule D |
| Mark-to-Market Rule | Yes, annually | No |
| Loss Carryover | Yes, offsets future gains | Yes, limited to $3,000/year |
| Wash Sale Rule | No | Yes |
Conclusion
Futures trading offers unique tax advantages, including the 60/40 capital gains tax treatment and the mark-to-market rule. However, traders must navigate complex IRS regulations and reporting requirements. By understanding these tax implications, traders can optimize their tax liabilities, avoid penalties, and enhance their overall profitability.
10 FAQs on Futures Trading Tax Implications
- How are futures contracts taxed in the U.S.?
- Futures contracts fall under IRS Section 1256, receiving a blended tax rate of 60% long-term and 40% short-term capital gains.
- What is the mark-to-market rule in futures trading?
- At the end of the tax year, all open futures contracts are marked to market, meaning unrealized gains/losses are taxed as if they were realized.
- Are futures traders subject to wash sale rules?
- No, futures traders are generally exempt from wash sale rules, unlike stock traders.
- What IRS forms do I need to report futures trading taxes?
- Traders must file IRS Form 6781 to report gains and losses from futures contracts.
- Do I need to pay taxes if I don’t close my futures position?
- Yes, due to the mark-to-market rule, unrealized gains/losses are taxed annually.
- Can I deduct futures trading losses?
- Yes, losses can offset gains, and excess losses may be carried forward to future tax years.
- Are there any tax benefits for professional futures traders?
- Professional traders may qualify for trader tax status (TTS), allowing business expense deductions.
- How does futures trading taxation compare to stock trading?
- Futures trading has a lower effective tax rate due to the 60/40 capital gains split, unlike stock trading, which follows standard capital gains rules.
- Are international futures traders subject to U.S. taxes?
- Non-U.S. traders may be subject to different tax regulations depending on their country of residence.
- How can I minimize my tax burden in futures trading?
- Keeping accurate records, utilizing tax loss harvesting, and consulting a tax professional can help minimize tax liabilities.
By staying informed about tax regulations and planning accordingly, futures traders can optimize their investment strategies while maintaining compliance with tax authorities.
For further details access our website:https://vibrantfinserv.com/
To visit:https://www.incometax.gov.in
Contact: 8130555124, 8130045124
Whatsapp: https://wa.me/918130555124
Mail ID: operations@vibrantfinserv.com
Web Link: https://vibrantfinserv.com
FB Link: https://fb.me/vibrantfinserv
Insta Link: https://www.instagram.com/vibrantfinserv2/