![]()
Sole Proprietorship Registration Process
Sole Proprietorship Registration Process
Introduction
Definition of Sole Proprietorship
Application Process for Sole Proprietorship Registration
The process of registering a sole proprietorship varies by country and jurisdiction, but the general steps include:
- Choose a Business Name: Select a unique name for the business and check for its availability.
- Register the Business Name (If Required): In some regions, sole proprietors must register their business name with local authorities.
- Obtain Necessary Licenses and Permits: Depending on the nature of the business, various permits or licenses may be required at the local, state, or national level.
- Apply for a Tax Registration Number: Obtain the necessary tax identification number (such as a GST or VAT registration, if applicable) from tax authorities.
- Open a Business Bank Account: It is advisable to separate personal and business finances by opening a dedicated bank account.
- Comply with Local Regulations: Some businesses may need additional compliance, such as zoning permits or professional licenses.
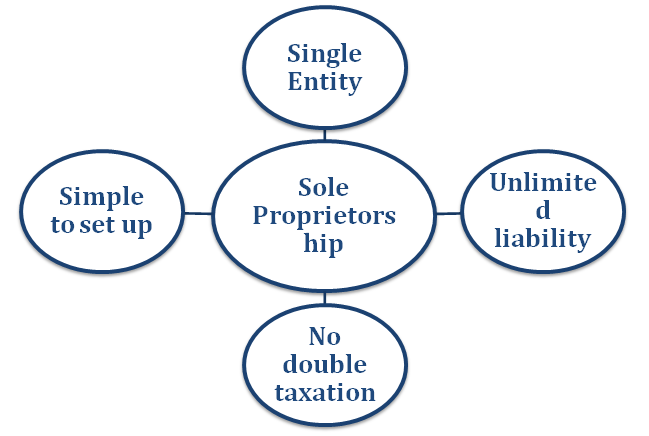
Benefits of Sole Proprietorship
- Easy to Set Up: Minimal legal formalities and paperwork make it one of the easiest business structures to establish.
- Low Cost: There are generally low initial registration and operational costs compared to other business entities.
- Full Control: The owner has complete control over decision-making and business operations.
- Tax Benefits: Sole proprietors may have tax advantages as profits are reported as personal income, avoiding double taxation.
- Flexible Management: No requirement for board meetings or complex compliance regulations.
Limitations of Sole Proprietorship
- Unlimited Liability: The owner is personally liable for all debts and legal actions against the business.
- Limited Capital: Raising funds can be challenging since banks and investors often prefer corporate structures.
- Limited Growth Potential: Expansion is restricted due to the dependency on personal resources and capabilities.
- No Business Continuity: The business ceases to exist upon the owner’s death or incapacity.
- Tax Burden: Higher tax rates may apply as business income is considered personal income in some jurisdictions.
Comparative Table: Sole Proprietorship vs. Other Business Structures
| Feature | Sole Proprietorship | Partnership | Corporation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Single Owner | Two or more owners | Shareholders |
| Liability | Unlimited | Shared liability | Limited liability |
| Registration Process | Simple & quick | Moderate | Complex |
| Decision-Making | Solely by owner | Joint decision-making | Board of directors |
| Taxation | Personal income tax | Personal income tax | Corporate tax |
| Continuity | Ends with owner’s death | May continue | Perpetual |
| Fundraising | Limited to personal funds | More funding options | Easier access to capital markets |
Conclusion
A sole proprietorship is an attractive option for entrepreneurs looking to start a business with minimal investment and regulatory requirements. While it offers advantages such as ease of setup, full control, and tax benefits, it also comes with risks like unlimited liability and limited access to capital. Entrepreneurs should carefully assess their long-term business goals and potential risks before opting for a sole proprietorship. Understanding the differences between business structures can help in making an informed decision that aligns with financial and operational objectives.
To visit https://www.incometax.gov.in
For further details access our website https://vibrantfinserv.com/
Contact:Â Â Â Â 8130555124, 8130045124
Whatsapp:Â Â https://wa.me/918130555124
Mail ID:Â Â Â Â Â Â operations@vibrantfinserv.com
Web Link:Â Â Â https://vibrantfinserv.com
FB Link:Â Â Â Â Â Â https://fb.me/vibrantfinserv
Insta Link:Â Â https://www.instagram.com/vibrantfinserv2/
FAQs:

For further details access our website https://vibrantfinserv.com