Project finance definition
Project finance is a method of financing large-scale projects, typically in infrastructure, energy, or industrial sectors, where the project itself serves as the primary source of repayment.
Here’s an overview of how project finance works:
Project Identification:
The first step is to identify a viable Project finance definition with potential economic returns. This could involve developing a power plant, constructing a transportation network, or building a manufacturing facility.
Structuring the Project:
Once the project is identify, a detailed project plan is create, including feasibility studies, technical assessments, financial projections, and risk assessments. The project structure is design, outlining the legal, contractual, and financial framework.
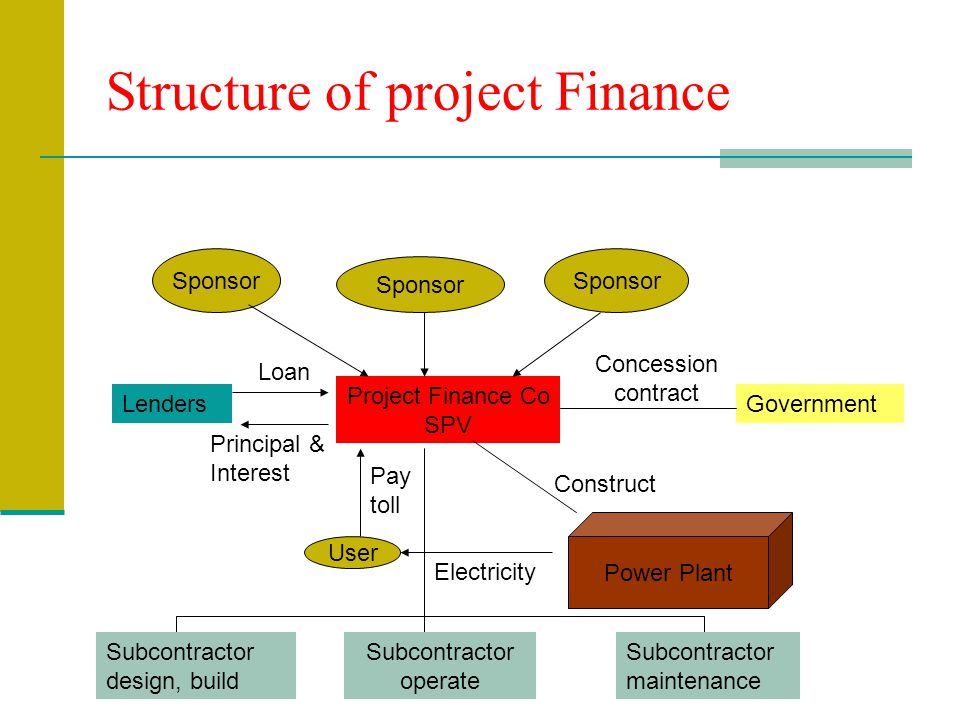
Consortium Formation:
Project sponsors (entities initiating the project) form a consortium that includes equity investors, lenders, contractors, and other stakeholders. Each party contributes their expertise, capital, or resources to the project.
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) Formation:
An SPV, also known as a project company, is create to manage the project’s operations and finances. The SPV is a separate legal entity, often with limited liability, established specifically for the project.
Financing Arrangements:
The project finance structure involves a combination of debt and equity financing. Lenders provide long-term loans based on the projected cash flows and assets of the project, while equity investors contribute funds in exchange for ownership shares in the SPV.
Risk Allocation:
Risks associated with the Project finance definition, such as construction delays, cost overruns, regulatory changes, or market uncertainties, are carefully assessed and allocate among the project stakeholders. Contracts and agreements are draft to define responsibilities, guarantees, and mitigations for identified risks.
Revenue Generation:
Once the project is operational, it generates revenue through the sale of goods or services, such as electricity, toll collection, or production output. These cash flows are used to repay the debt, cover operating expenses, and provide returns to equity investors.
Repayment and Return on Investment:
The project’s cash flows are use to repay the project debt, including interest and principal. Equity investors receive returns on their investment through dividends, share appreciation, or other agreed-upon mechanisms.
Project Lifecycle and Exit:
The project finance arrangement typically spans the project’s lifecycle, which can range from several years to decades. Upon completion of the project and repayment of debt, the SPV may be dissolve, or ownership may be transfer to a new entity.
Project finance structures provide several benefits, including ring-fencing project risks, leveraging the project’s assets for financing, and attracting long-term investors. However, it requires careful evaluation of risks, thorough due diligence, and effective risk management to ensure the project’s success and financial viability.”
For more information visit this site: https://www.incometax.gov.in
FAQs
1. What is project finance?
- Project finance is a method of funding where the repayment comes primarily from the project’s cash flow rather than the sponsor’s balance sheet.
2.What are the key components of a project finance deal?
- Key components include the project’s cash flow, financing structure, risk allocation, and contracts.
3.How is risk managed in project finance?
- Risk is managed through detailed contracts, insurance, and careful structuring of the finance deal to ensure each risk is assigned to the party best able to handle it.
4.What is a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)?
- An SPV is a separate legal entity create to isolate financial risk and manage the project’s operations and funding.
5.What is the role of equity in project finance?
- Equity represents ownership in the project and is provide by investors seeking a return based on the project’s success.
6.How does debt financing work in project finance?
- Debt financing involves borrowing money that must be repay with interest. Lenders are repay from the project’s cash flow.
7.What is a project’s cash flow?
- Cash flow refers to the net amount of cash being generated by the project, which is use to repay debts and provide returns to equity investors.
8.What are the common sources of project finance?
- Common sources include commercial banks, investment banks, private equity firms, and development banks.
9.What role do contracts play in project finance?
- Contracts outline the terms between parties involved, such as construction, operation, and supply agreements, ensuring clarity and accountability.
10. What is due diligence in project finance?
- Due diligence involves a thorough evaluation of the project’s feasibility, risks, and financial projections to ensure it is a sound investment.