User Intent
Users searching for “What are internal liabilities?” want a clear understanding of this financial concept, its applications, benefits, and limitations. They may be business owners, finance students, or investors looking to manage liabilities effectively.
Introduction
Every business and financial institution operates with a mix of assets and liabilities. While external liabilities are widely discussed, internal liabilities are equally important in managing an organization’s financial health. Understanding internal liabilities helps businesses ensure smoother operations and financial stability.
In this article, we will explore what internal liabilities are, their applications, benefits, limitations, and a comparative analysis to provide a comprehensive understanding.
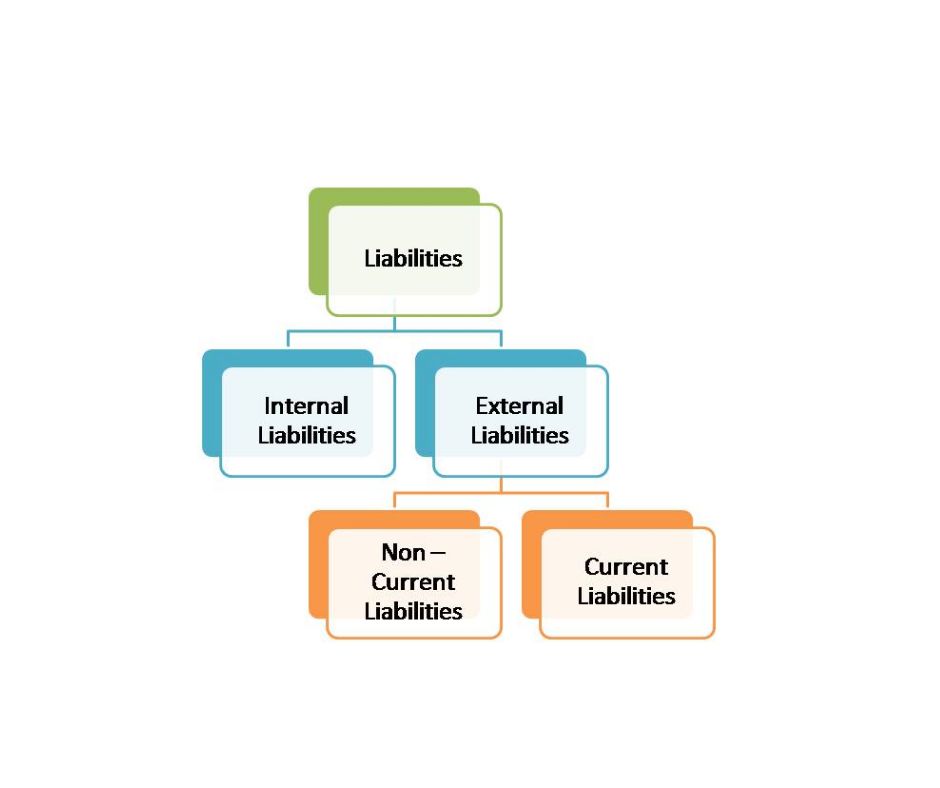
Definition of Internal Liabilities
Internal liabilities refer to the financial obligations a company owes to its internal stakeholders, such as owners, employees, and shareholders. Unlike external liabilities, which involve third parties like banks or creditors, internal liabilities originate within the company.
Examples of internal liabilities include:
- Retained earnings
- Employee benefits payable
- Accrued expenses
- Provisions for dividends
- Owner’s equity
These liabilities represent commitments a business must fulfill using its internal resources rather than external borrowing.
Application of Internal Liabilities
Internal liabilities play a crucial role in financial planning, decision-making, and operational management. Their applications include:
- Business Growth and Expansion
- Retained earnings, a form of internal liability, are often reinvested to expand operations, launch new products, or acquire assets without external borrowing.
- Employee Compensation and Benefits
- Accrued salaries and benefits payable ensure employees receive their dues, boosting workforce morale and efficiency.
- Shareholder Distributions
- Companies allocate funds for dividends from internal liabilities to ensure stakeholders receive their share of profits.
- Financial Stability and Risk Management
- Businesses use internal liabilities to manage risks and uncertainties by setting aside provisions for contingencies, reducing dependency on external loans.
Benefits of Internal Liabilities
- Reduced Financial Risk
- Unlike external liabilities, internal liabilities do not involve external lenders, lowering financial risks and interest burdens.
- Better Control Over Funds
- Companies have full autonomy in managing internal liabilities, allowing flexible financial planning.
- Cost-Effective Financing
- Using retained earnings or other internal sources eliminates interest expenses, making financing more affordable.
- Improved Creditworthiness
- Lower external debts due to reliance on internal liabilities enhance a company’s credit rating.
- Business Sustainability
- Efficiently managing internal liabilities ensures long-term sustainability without excessive reliance on external funding.
Limitations of Internal Liabilities
- Limited Availability of Funds
- Internal liabilities depend on internal resources, which may not always be sufficient for large-scale expansion.
- Slower Growth Potential
- Companies relying solely on internal liabilities may experience slower growth compared to businesses using external financing.
- Possible Mismanagement
- Poor management of retained earnings or accrued expenses can lead to financial inefficiencies.
- Equity Dilution Risks
- If owners withdraw more funds from the business, it can reduce reinvestment opportunities.
Comparative Analysis: Internal vs. External Liabilities
| Factor | Internal Liabilities | External Liabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Within the company (owners, employees) | Outside entities (banks, creditors) |
| Examples | Retained earnings, accrued expenses | Loans, bonds, accounts payable |
| Interest Cost | No interest payable | Interest costs apply |
| Financial Risk | Lower risk | Higher risk due to repayments |
| Growth Potential | Slower, depends on internal funds | Faster, allows large investments |
| Control | Full control over usage | Subject to lender conditions |
| Credit Impact | Improves creditworthiness | Can impact credit rating |
Conclusion
Internal liabilities are an integral part of business finance, providing cost-effective, risk-free funding sources. While they offer advantages such as better financial control and sustainability, they also come with limitations like restricted growth potential. A balanced approach—leveraging both internal and external liabilities—ensures financial stability and long-term success.
By understanding and managing internal liabilities effectively, businesses can optimize their financial health, minimize risks, and achieve sustainable growth.
FAQs
- What are examples of internal liabilities?
- Internal liabilities include retained earnings, accrued salaries, provisions for dividends, and employee benefits payable.
- How do internal liabilities differ from external liabilities?
- Internal liabilities arise within the company (from owners or employees), while external liabilities involve third parties like creditors and banks.
- Are internal liabilities recorded in financial statements?
- Yes, they are recorded under liabilities and equity sections of the balance sheet.
- Can a company operate solely on internal liabilities?
- While possible, relying only on internal liabilities may limit growth opportunities due to restricted funding.
- How do internal liabilities impact business sustainability?
- They help maintain financial stability without accumulating external debt, supporting long-term sustainability.


