![]()
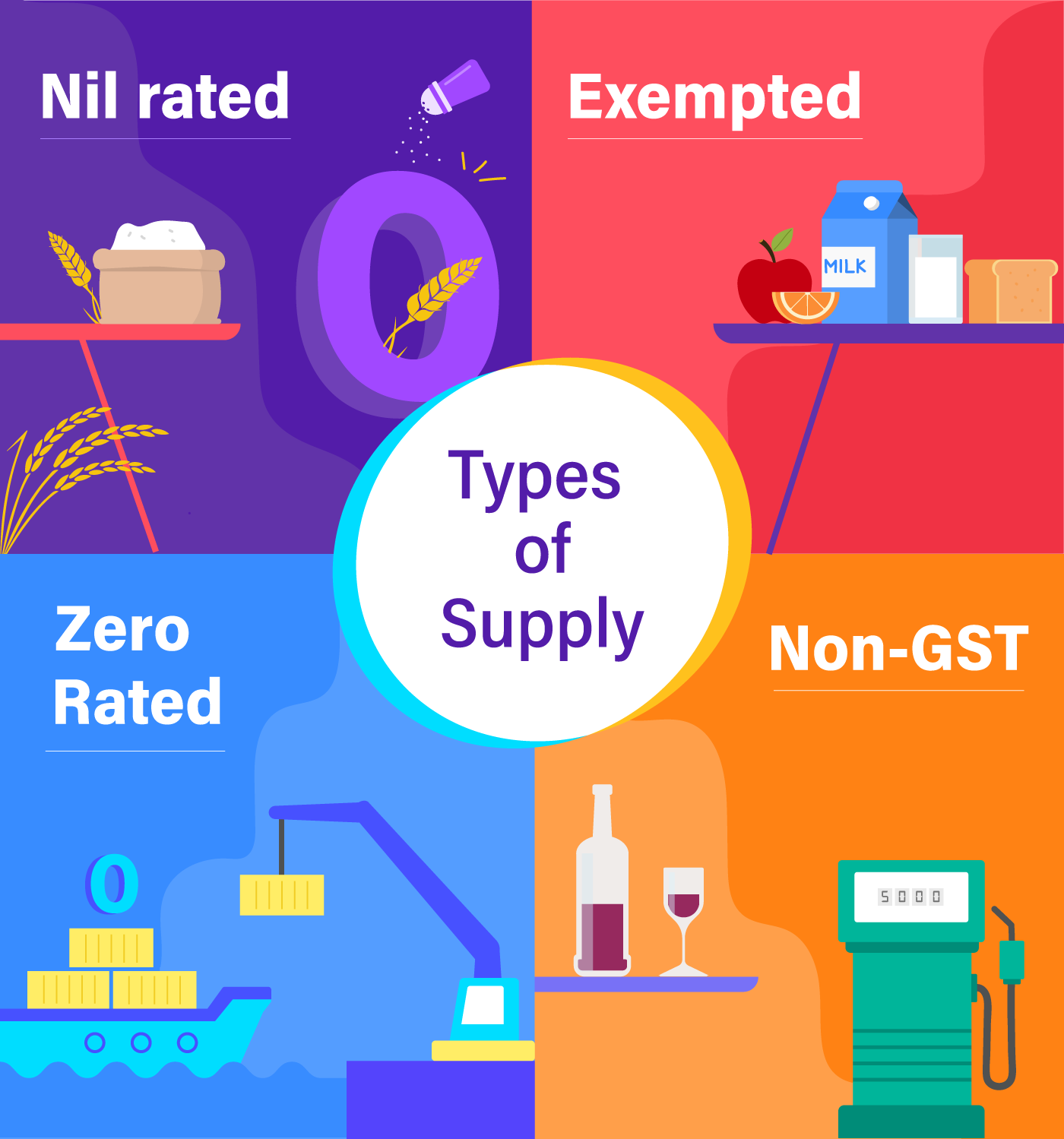
Table of Contents
ToggleGST non-exempt categories
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a value-added tax applied on the supply of goods and services in many countries. While some goods and services are exempt from GST, most fall under non-exempt categories that are subject to GST. Understanding these non-exempt categories is crucial for businesses to remain compliant and for consumers to know which goods and services will have GST added to their final cost.
In this article, we will explore the types of goods and services that fall under GST non-exempt categories, the applicable rates, and what this means for businesses and consumers.
What are GST Non-Exempt Categories?
GST non-exempt categories refer to goods and services that are subject to GST at the applicable tax rates. These categories generally encompass the majority of commercial transactions and are taxed at rates ranging from 5% to 28%, depending on the country and the type of goods or services involved. For example, many consumer goods, luxury items, and certain services such as consultancy or transportation are considered non-exempt.
Common GST Non-Exempt Categories
Here is a breakdown of the most common GST non-exempt categories:
1. Consumer Goods
- Electronics: Laptops, smartphones, and home appliances like refrigerators and washing machines are non-exempt.
- Clothing and Footwear: While basic or essential clothing may be exempt in some countries, luxury or branded apparel and footwear typically fall under non-exempt categories.
- Luxury Items: Products like designer clothing, high-end automobiles, and jewelry often attract the highest GST rates.
2. Services
- Professional Services: Fees for legal, consultancy, audit, and financial services are generally non-exempt from GST.
- Telecommunication Services: Mobile and internet services are subject to GST.
- Transportation Services: Air, rail, and road transportation services, excluding local public transport, are commonly taxed under GST.
3. Automobiles
- Both personal and commercial vehicles are subject to GST. The rate varies based on the vehicle type, with higher GST applied to luxury cars and SUVs compared to smaller or commercial vehicles.
4. Food and Beverages
- Packaged Foods: Most processed or packaged foods, including snacks, soft drinks, and instant meals, fall under non-exempt categories.
- Dining Out: Restaurants, cafes, and food delivery services are subject to GST, with different rates for different types of establishments.
5. Real Estate
- Commercial Property: Sales of commercial real estate, including office spaces and shops, typically attract GST.
- Rental Income: Commercial rental income is also subject to GST in most countries.
6. Healthcare Services (Non-Essential)
- While basic healthcare services like doctor consultations and emergency treatments are often exempt, non-essential or luxury healthcare services, such as cosmetic surgery, may be taxed under GST.
7. Entertainment and Media
- Movies and Theatres: Tickets for movies, plays, and other entertainment events are subject to GST.
- Digital Content: Online streaming services and digital content subscriptions, such as Netflix, Amazon Prime, or digital newspapers, fall under GST non-exempt categories.
8. Construction and Infrastructure
- GST applies to contracts and services related to construction and infrastructure projects. The materials used in construction, such as cement, bricks, and steel, also fall under non-exempt categories.
GST Rates for Non-Exempt
The GST rate for non exempt categories varies depending on the product or service in question and the country’s specific GST structure. Typically, there are different slabs, such as:
- 5%: Generally applies to essential goods and services.
- 12%: Intermediate category for goods like processed food and some types of appliances.
- 18%: Commonly applied to most goods and services, including electronics, clothing, and professional services.
- 28%: The highest slab, reserved for luxury goods, high-end automobiles, and entertainment services.
It is important for businesses to know the exact GST rates applicable to their products or services to calculate the correct amount of tax to be charged to consumers.
Implications for Businesses
Businesses dealing in non-exempt categories must ensure that they charge the correct GST rates and file their returns in compliance with tax laws. Here are the key implications:
1. Tax Collection and Compliance
Businesses must collect GST from customers at the point of sale and remit it to the government. They also need to maintain proper records for all taxable transactions and file GST returns on time.
2. Input Tax Credit (ITC)
Businesses that are GST-registered and deal in non-exempt goods or services are eligible to claim an Input Tax Credit (ITC) on the GST paid for purchases or inputs used in their business. This helps to reduce their overall tax liability.
3. Pricing and Transparency
Businesses must clearly display GST-inclusive prices to consumers. The transparency of tax charges helps consumers understand the total cost of the goods or services they are purchasing.
Impact on Consumers
For consumers, goods and services falling under non-exempt categories will have GST added to the final purchase price. This means the price you pay at the store or for a service will include the applicable GST. Understanding which categories are non-exempt can help you anticipate the total cost and make more informed purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
Understanding GST non-exempt categories is crucial for both businesses and consumers. These categories cover the majority of goods and services we encounter in daily life, including electronics, professional services, and dining out. Businesses must ensure compliance with GST laws, including charging the correct rate and filing returns on time, while consumers should be aware that GST will be added to the price of non-exempt items. Keeping up with GST regulations helps both parties avoid penalties and ensures smooth transactions.
FAQs:
1. What is GST?
GST (Goods and Services Tax) is a value-added tax imposed on the supply of goods and services at every stage of the supply chain, with credit for taxes paid on inputs.
2. How do I apply for a GST number?
You can apply for a GST number online through your country’s official tax portal by providing business details, PAN, and other relevant documents.
3. What is the difference between a tax exemption and a tax deduction?
A tax exemption eliminates certain income from being taxed, while a tax deduction reduces the taxable income, lowering the amount of tax payable.
4. Can I claim input tax credit (ITC) on exempt goods?
No, input tax credit cannot be claimed on goods or services that are exempt from GST.
5. What is Form 16?
Form 16 is a certificate provided by employers to employees, showing details of salary paid and tax deducted at source (TDS) during the financial year.
6. How often should I file GST returns?
GST returns are usually filed monthly or quarterly, depending on your business turnover and the applicable tax laws in your country.
7. What is an ITR (Income Tax Return)?
ITR is a form filed with the tax department declaring income earned during the financial year, which helps in assessing the tax liability.
8. What is the penalty for late filing of taxes?
The penalty for late filing of taxes varies, but typically includes late fees, interest on unpaid tax, and sometimes additional fines.
9. Are there any goods that are exempt from GST?
Yes, certain essential goods like fresh fruits, vegetables, and basic food grains may be exempt from GST, depending on the jurisdiction.
10. Can I e-verify my income tax return?
Yes, you can e-verify your income tax return using methods like Aadhaar OTP, net banking, or through a digital signature.
