
![]()
Fixed Deposit Interest Rate
A Fixed Deposit (FD) serves as a financial instrument offered by banks and various financial institutions, enabling individuals to invest a specified amount for a predetermined duration at a fixed interest rate. Fixed Deposits are known for their safety, stability, and guaranteed returns.
Key Features of Fixed Deposits:
1. Interest Rates:
Fixed Deposits provide a consistent interest rate for a specified period. The rates vary between banks and are influenced by the tenure of the deposit.
2. Tenure:
Fixed Deposits come with a predetermined duration, spanning from a short few days to an extended period of several years. Depositors select the tenure aligned with their financial objectives.
3. Minimum and Maximum Deposit Amount:
The minimum deposit amount required to open an FD varies across banks. There is generally no upper limit, allowing investors to deposit large sums.
4. Interest Payment Frequency:
Interest can be pay out at different intervals: monthly, quarterly, annually, or at maturity, depending on the terms of the FD.
5. Cumulative vs. Non-Cumulative FDs:
In cumulative FDs, the interest is compound and paid along with the principal at maturity. In non-cumulative FDs, interest is paid out regularly, providing a source of income.
6. Premature Withdrawal:
Premature withdrawal of FDs is allowed, but it often comes with a penalty in the form of reduced interest rates. Some banks may restrict premature withdrawal for certain tenures.
7. Tax Implications:
The interest earned on Fixed Deposits is subject to taxation based on the individual’s income tax slab. Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) comes into play when the interest surpasses a predetermined threshold.
8. Loan Against FD:
Some banks offer the facility of taking loans against FDs. The loan amount is usually a percentage of the FD value and carries a lower interest rate compared to personal loans.
9. Nomination Facility:
Depositors can nominate a beneficiary who will receive the FD amount in case of the depositor’s demise.
10. Auto-Renewal Option:
Banks often provide an auto-renewal facility, wherein the FD is renewed for the same tenure at the prevailing interest rate unless the depositor instructs otherwise.
For more information visit: https://www.rbi.org.in
Advantages of Fixed Deposits: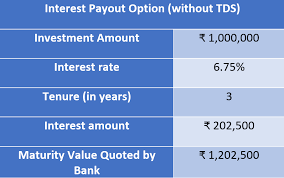
1. Safety:
FDs are considered a safe investment option as they are backed by the guarantee of the issuing bank.
2. Stable Returns:
The fixed interest rate guarantees a predictable return on investment
3. Diverse Tenures:
FDs offer flexibility in choosing tenures, allowing investors to align their investments with financial goals.
4. Liquidity:
While premature withdrawal may come with penalties, FDs still offer a degree of liquidity compare to long-term investments.
5. Ideal for Risk-Averse Investors:
FDs are suitable for investors who prioritize capital protection and a steady income stream. Considerations:
6. Inflation Risk:
The returns from FDs may not always outpace inflation, potentially reducing real returns.
7. Tax Efficiency:
Investors need to consider the tax implications, especially if they fall into higher tax brackets.
8. Opportunity Cost:
FD returns might be lower compared to riskier investment options, and investors should weigh the opportunity cost.
9. Interest Rate Risk:
1. FD interest rates are fixed at the time of investment, and changes in market interest rates won’t impact existing FDs.
2. Fixed deposit interest rates can vary between banks and financial institutions. The rates are subject to change based on economic conditions and policies set by the respective banks.
3. It’s important to note that interest rates can fluctuate, and the rates mentioned here might not be current.
To obtain the most accurate and up-to-date information, you should directly check with the specific bank or financial institution where you are considering opening a fixed deposit account.
Typically, fixed deposit interest rates are expressed on an annual basis.
Here are some general trends:
1. Nationalized Banks:
Public sector or nationalized banks in India often offer competitive fixed deposit interest rates. The rates may vary for different tenures.
2. Private Banks:
Private banks, including both Indian and international banks, may offer slightly higher interest rates compared to nationalized banks. These rates can vary based on the bank’s policies.
3. Small Finance Banks and NBFCs:
Small finance banks and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) may also provide fix deposit options with attractive interest rates, although they might be higher-risk compared to traditional banks.
4. Senior Citizen Rates:
Many banks provide higher interest rates on fixed deposits for senior citizens. These rates are generally 0.25% to 0.75% higher than the standard rates.
5. Interest Payout Frequency:
Some banks allow customers to choose the frequency of interest payouts (monthly, quarterly, annually) when setting up a fixed deposit.
It’s advisable to compare the interest rates, tenure options, and terms offered by different banks before making a decision. Additionally, consider factors such as the credibility of the institution, the reputation of the bank, and any associated terms and conditions.
In conclusion, Fixed Deposits are a conservative investment choice suitable for those seeking stability and assured returns.
Also visit our site: https://vibrantfinserv.com/